In the previous posts, we have discussed robots and types of robots. I think that may generate some curiosity and interest in you to build robots. If you have an interest in building a robot, how to learn it? This post mainly discussing that topic.
What is Robotics?
Here is my understanding of Robotics.
“Robotics is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering which deals with the conception, design, simulation, and manufacturing of a robotic system. ”
In the definition, we can see that robotics is an ‘interdisciplinary‘ branch of engineering meaning it is the combination of many branches of engineering. In order to build robots, you have to learn robotics engineering. You will learn the following things in robotics engineering to build a robot.
1. Robot designing

Designing robots requires knowledge and experience in many fields of engineering. Developing concepts and designing is the first step in robot building. You may get a set of requirements that have to be done by the robot. The robotics engineer can able to develop a blueprint of the design by planning the robot components, electronic circuits, motors, sensors and everything which is satisfying the requirements.
2. 3D Modeling
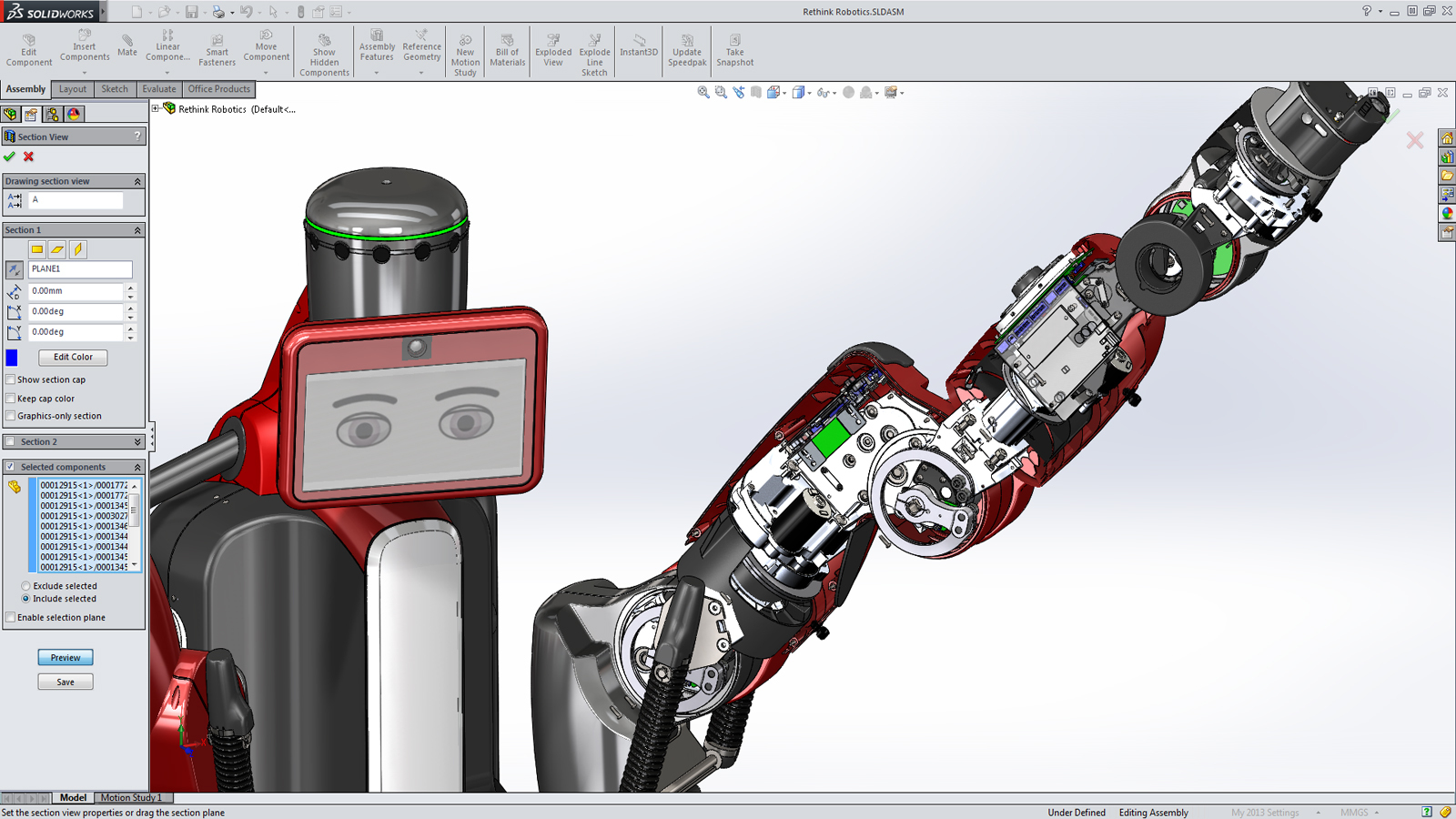
The designed robot has to model using CAD software tools such as SolidWorks, Catia, etc to find the design flaws and perfect it. In order to do 3D modeling, the robotic engineer has to know about mechanical engineering concepts.
3. Simulation

This phase will give life to the virtual 3D robot model. You can assign the actual robot parameters in simulation so that you can verify the working of the robot in the real world. It is a mandatory step to simulate the robot behavior before prototyping the robot hardware. It can save a lot of time and money in robot development. If you avoid the simulation, it can end in a wrong robot prototype.
You may require knowledge in mechanical engineering as well as computer engineering in order to simulate a robot. Here are a few free robot simulation software available: Gazebo, Webots, V-REP, etc.
4. Prototyping
After verifying robot design and working of the robot in simulation, you can start prototype the robot parts, which include robot chassis, sensors, computing units and actuators for the robot. Nowadays, a quick method of doing prototyping is using 3D printing. After 3D printing the robot chassis and buying the robot components, we can assemble the ‘Sense->Think->Act’ components of the robot to the robot chassis.
In order to prototype the hardware of the robot, we should know about electronics engineering and circuit designing.
5. Robot Software
After prototyping the robot hardware, the next step is to give life to the robot. The heart of the robot is a computer, and you have to program the robot to move. There are various robot software frameworks available like ROS to program a robot. The commonly used programming languages for programming robots are C++ and Python. There may be microcontrollers inside the robot, so you can use embedded C, Arduino programming, etc to program those controllers.


Hi, I read your essay, and what I really liked about it was that it was helpful and to the point. This helped me learn more about robots. I’d like to read more posts on your website.
Robotics has emerged as a fascinating field that combines engineering, computer science, and artificial intelligence to create intelligent machines capable of performing tasks autonomously or with minimal human intervention. It has revolutionized various industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to space exploration and entertainment.